Basic journalism
Our basics section provides foundational knowledge for journalists starting their careers and for those wanting to refresh their skills. Learn techniques including news writing, interviewing, story structure, and reporting practices that form the bedrock of quality journalism. All our material is free to download, adapt and use. Scroll down our site map for all the content in this and other sections.
Writing a radio news script
Radio journalists must write clear scripts that weave together compelling audio clips, ensuring listeners understand a news story's significance.
Where does news come from?
The job of the journalist is to uncover the stories that shape our understanding of the world. Here we look at what makes news.
Fact-checking and adding context
An essential part of the editorial process is to examine everything we are told to make sure it is factual.
Gender equality in the media
The role of the journalist in rectifying gender imbalance in media is multifaceted, and it involves both individual actions and contributing to broader systemic change.
Translation in journalism
If you are a journalist working in a multilingual society, you may have to work in more than one language.
Parliamentary reporting for beginners
To cover Parliament, a journalist must master local laws, procedure, and political parties, backed by a solid grasp of history.
The qualities of a journalist
Journalism is a demanding profession that requires a unique combination of intellectual curiosity, linguistic skill, and a deep understanding of the world.
What editors look for when hiring
What's the best preparation for a career in journalism? Media Helping Media asked some experts in the field what they look for when hiring staff.
The power of words
Journalists need to understand the power of using the right words when writing news stories
Where does news come from?
The job of the journalist is to uncover the stories that shape our understanding of the world. Here we look at what makes news.
Covering a news event
Check our news event coverage guide with tips on preparation, on-site reporting, ethical interviews, and capturing compelling photos and video.
Producing a radio news bulletin
Crafting a radio bulletin is like serving a balanced meal: it must be nourishing, digestible, and leave your audience perfectly prepared for the day ahead.
Using the right words
Words are the essential tools of journalism. They convey meaning and help the audience understand the issues we are covering. So they need to be used properly.
Developing news sense
How do we know what is “news”? There are millions of things going on in the world all the time and only some of them become news stories.
Writing a radio news script
Radio journalists must write clear scripts that weave together compelling audio clips, ensuring listeners understand a news story's significance.
Adjectives and adverbs in journalism
When it comes to writing - not just news writing but any kind of writing - adjectives and adverbs have a bad reputation.
Creating a structured news report
Writing a news item without a plan is like building a kit without instructions. You need a structured story plan to order your facts logically and engage readers.
The power of quotes in journalism
Quotes can define an era, a person, or a story. Used thoughtfully, they transform reporting from factual to memorable, from clear to compelling.
Attribution and plagiarism
Producing a piece of original journalism involves uncovering facts that, had it not been for you, would have remained hidden.
What is news?
What is news? Beyond facts, it’s the stories that truly matter to people. Explore why human interest and personal relevance are at the heart of every headline.
Interviewing remotely
Here we explore the key issues journalists face when interviewing sources via electronic media instead of face-to-face and in real time.
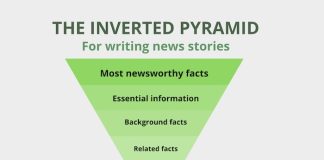
The inverted pyramid
The inverted pyramid model puts key news first, followed by supporting details, with the least important background information at the base of the article.